Which Best Describes How Meiosis Contributes to Genetic Variation
One sister chromatid on each chromosome should appear to have undergone crossing over. The simplest form of genetic variation one might observe at a single nucleotide site is a difference in the nucleotide base present whether adenine cytosine guanine or thymine.

How Does Meiosis Contribute To Genetic Diversity Lisbdnet Com
These types of variants are called single nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs and they are the most common.

. One of the best characterised imprinted regions is located close to the centromere on the long arm of chromosome 15 15q112. A Further genetic variation typically does not occur after meiosis I. The meiotic stability of the AABBAA 2n6x42 amphiploids suggests an ease of maintenance of these genetic stocks.
Often structural variants SVs are defined as variants of 50 base pairs bp or greater such as deletions duplications insertions inversions and other rearrangements. Concept 133 Meiosis reduces the number of chromosome sets from. And MII that separates resulting sister.
Structural variation refers to genetic variants that affect larger segments of the human genome as opposed to point mutations. Only mitosis allows for the possibility of translocation. Each cell should contain one large duplicated chromosome and one small duplicated chromosome.
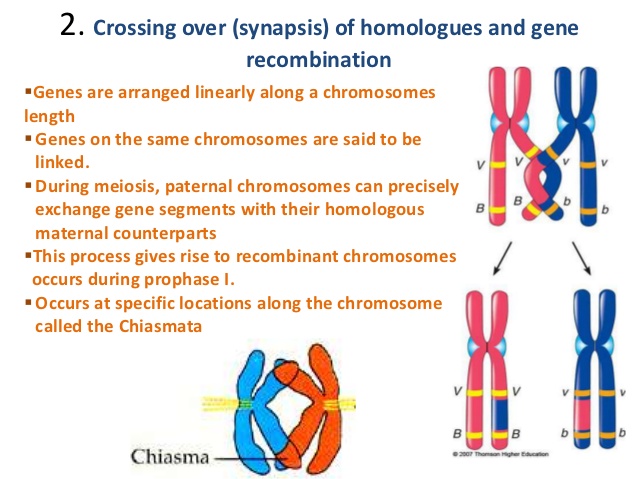
Although energetically more costly than asexual reproduction sexual reproduction leads to different combinations of alleles that could provide adaptability in a changing environment. The DDR also plays a key role in generating genetic diversity via sexual reproduction a stage in which is meiosis the cell-division pathway that generates haploid gametes. In sexual reproduction chromosomes can sometimes swap sections during the process of meiosis cell division thereby creating new genetic combinations and thus more genetic variation.
About 90 of structural variants are noncoding deletions but most individuals. Concept 134 Genetic variation produced in sexual life cycles contributes to evolution. MI that reductionally-segregates the two copies of individual chromosomes.
While meiosis shows genetic diversity. Meiosis of F1 hybrids 2n3x21 ABA with up to six bivalents for metaphase I chromosome associations per meiocyte is indicative of genomic exchange among the A genomes. There are a number of genetic conditions which are related to imprinting including BeckwithWiedemann syndrome SilverRussell syndrome Angelman syndrome AS and PraderWilli syndrome PWS.
Assess how meiosis contributes to genetic variation while mitosis does not. Only meiosis allows for the possibility of gene point mutations. Following DNA replication meiosis proceeds by two successive cell divisions.
Genetic variation is an important force in evolution as it allows natural selection to increase or decrease frequency of alleles already in the population. Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite. Refer to Figure 62 for visual answers.
Diploid to haploid. Sexual reproduction increases genetic variation within a species. Genetic variation is any difference between two copies of the same gene or DNA molecule.
New combinations of alleles 3. Why meiosis leads to significant genetic variation while mitosis does not. The process by which cells replicate is very different than the process by.
IDENTIFICATION OF INHERITED DISEASES Conventional genetic tests Phenotype analysis Chromosome analysis and Karyotyping. Which of the following statements best describes the advantage that sexual reproduction likely provides over asexual reproduction. B Meiosis II is essentially the same process as mitosis except the starting cells are haploid n.
Meiosis is a form of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms wherein two consecutive nuclear divisions meiosis I and meiosis II occur without the chromosomal replication in between leading to the production of four haploid gametes each containing one of every pair of homologous chromosomes that is with the maternal and paternal chromosomes. The durum cultivars in these amphiploids are susceptible for. C Meiosis II is essentially the same process as mitosis except the genetic material will not replicate before division takes place.
Concept 132 Fertilization and meiosis alternate in sexual life cycles. Adaptation is an observable fact of life accepted by philosophers and natural historians from ancient times independently of their views on evolution but their explanations differed. Empedocles did not believe that adaptation required a final cause a purpose but thought that it came about naturally since such things survived Aristotle did believe in final causes but.
MEIOSIS AND GENETIC VARIATION 1. MOLECULAR CHARACTERIZATION OF HUMAN GENETICS DISORDERS Human Genome. Although DNA replication is tightly regulated and remarkably accurate errors do occur and result in mutations which are also a source of genetic variation.
How Does Meiosis Create Genetic Diversity Socratic

The Purpose Of Mitosis Includes All Of The Following Except 5a Ppt Download
No comments for "Which Best Describes How Meiosis Contributes to Genetic Variation"
Post a Comment